
355 nm Cold Laser Successfully Opens Blocked Vessels: Xuanwu Hospital & Vivolight Medical In Vitro Study
Recently, a research paper titled “An in vitro feasibility study of 355 nm laser atherectomy for the treatment of peripheral atherosclerotic lesions”, co-authored by the team of Dr. Jianming Guo from the Vascular Surgery Department of Xuanwu Hospital Capital Medical University and Vivolight Medical, was published in the Journal of biophotonics. This study used Vivolight Medical's self-developed 355 nm laser ablation device (CLA-355), to demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the 355 nm laser for the ablation of different types of vascular plaque, and successfully opened completely occluded blood vessel!
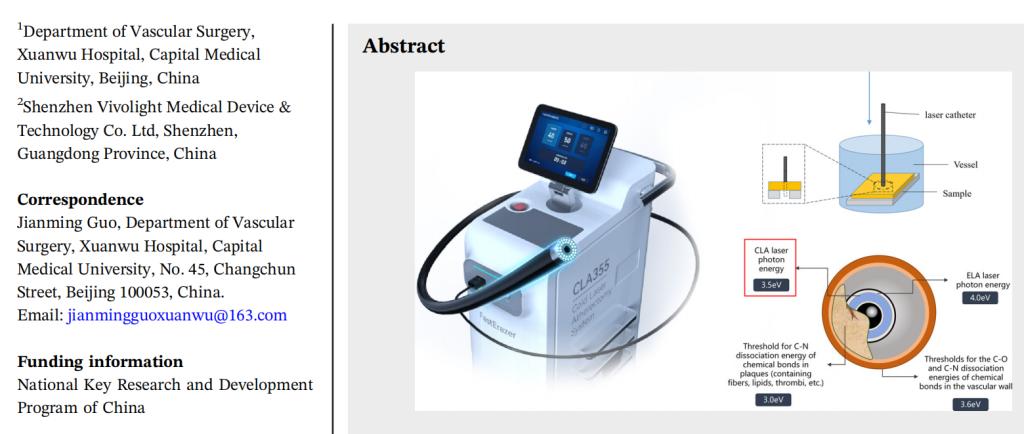
Background of the Study
In China, 42 to 60 million patients suffer from limb ischemia caused by lower extremity arterial occlusion. Late-stage patients may face the risk of amputation due to ischemic ulcers and gangrene. The current mainstream treatment is stenting, which has clear short- & medium-term effects, but long-term issues such as stent fracture and restenosis remain.
Laser ablation technology offers an alternative to stent implantation. The laser device fragments the plaque into particles smaller than 25 µm, which are then ablated and dissolved. Although the 308 nm laser is widely used, its high absorption coefficient when in contact with blood or contrast agents can lead to vascular damage. Therefore, researchers have proposed the use of a 355 nm solid-state laser, which offers higher ablation efficiency and lower risk of damage to the vascular wall, while being compatible with contrast agents. However, the safety and efficacy of the 355 nm laser in clinical applications require further study. Experimental Results This study used the 355 nm laser ablation device (CLA-355) developed by Vivolight Medical, and the ablation experiments were conducted by the team of Dr. Jianming Guo from Xuanwu Hospital's Vascular Surgery Department. The study verified the efficacy of the 355 nm laser for the ablation of various types of vascular plaque, providing important guidance and evidence for its clinical application in treating peripheral atherosclerotic lesions:
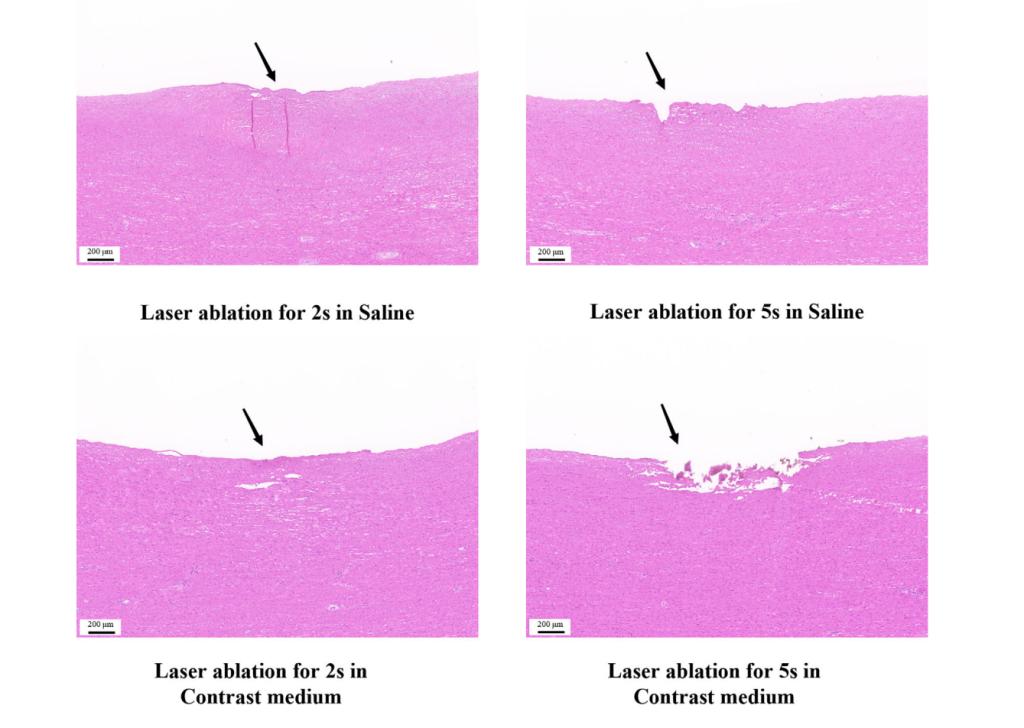
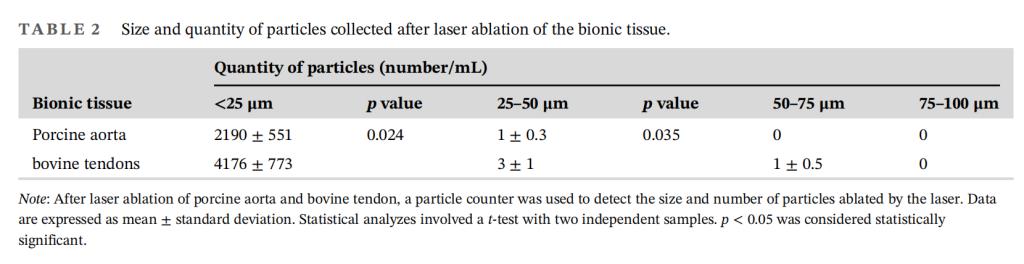
2. High safety: The proportion of particles smaller than 25 µm produced after laser ablation on porcine aorta and bovine Achilles tendon exceeded 99%, ensuring no risk of distal arterial embolism.
3. Successful opening of three types of plaque: The 355 nm laser successfully opened chronic total occlusion, in-stent restenosis, and old thrombus plaques in human specimens.
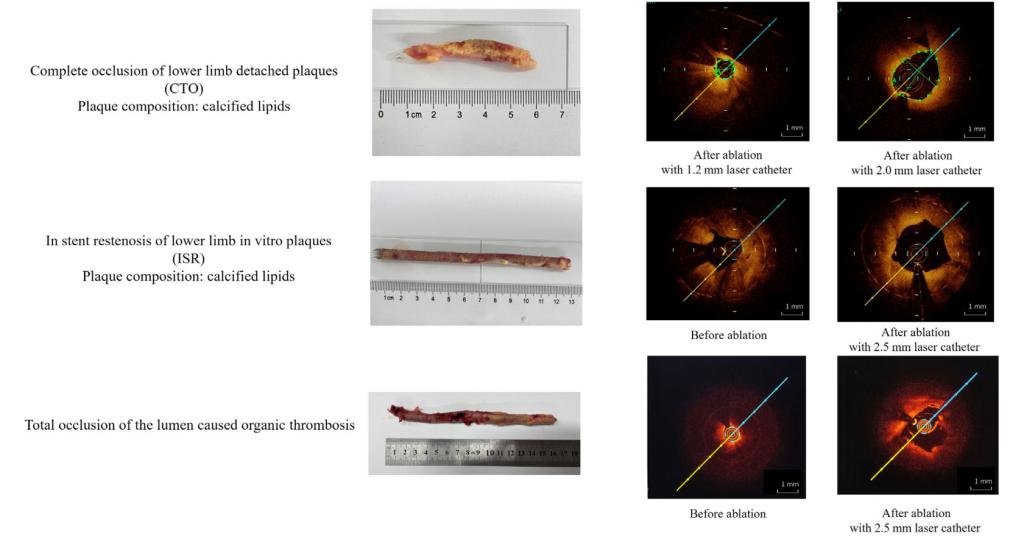
4. Compatibility with contrast agents: The 355 nm laser can work effectively in an environment compatible with contrast agents, which is a significant advantage in clinical applications, allowing simultaneous imaging examinations during laser treatment.
5. Safety and portability: Compared with the 308 nm excimer gas laser (which contains toxic gases), the 355 nm solid-state laser device is safer, smaller, lighter, and more portable.
Medical-Engineering Collaboration
This publication is one of the collaborative achievements between the Vascular Surgery Department of Xuanwu Hospital and Vivolight Medical. Vivolight Medical is dedicated to the cutting-edge development of laser technology and is committed to transforming laboratory research results into medical products for clinical use. Xuanwu Hospital provided valuable clinical experience during the experiment, and the continuous exchange and collaboration between the two parties sparked a deep integration of medical and engineering knowledge, further optimizing the device’s functionality, leading to impressive experimental results. This was crucial during the early validation phase of the product. Meanwhile, the trust and understanding established between the doctors and the company greatly facilitated the subsequent formal clinical trials.
Moreover, this collaboration will yield multiple clinical research reports and patent applications in the future. Looking ahead, Vivolight Medical will continue to uphold the concept of "medical-engineering integration", strengthen collaboration and exchange with major medical institutions, accelerate the transformation and application of innovative medical technologies, and promote the continuous development of diagnostic and treatment technologies in the field of vascular diseases.
Leave A Message
Scan to WhatsApp :
