
IPA: A Breakthrough in Diagnosing Vulnerable Plaques and Advancing Cardiovascular Care
A recent study published in The Lancet on the PREVENT trial shows that for patients with vulnerable coronary plaques, even when the stenosis (narrowing) isn’t severe, preventive percutaneous coronary intervention in addition to optimal medical therapy can significantly reduce the risk of adverse cardiac events and mortality. This research provides compelling new evidence for detecting vulnerable plaques and using protective intervention strategies, igniting widespread discussion on tools for detecting these high-risk plaques.The ability to comprehensively identify and manage vulnerable plaques is key to optimizing interventional diagnosis and treatment, and reducing the risk of major cardiovascular events in acute coronary syndrome.
With continuous advancements in imaging technology, methods for identifying and assessing vulnerable plaques have been evolving rapidly. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT), have made strides in visualizing the fine structures of these plaques. OCT offers unparalleled high-resolution imaging, enabling the detection of microscopic characteristics like fibrous cap thickness, cholesterol crystals, and macrophage presence. However, interpreting these images can vary across physicians, and manual measurements often introduce inconsistencies. This variability presents a challenge in maintaining the accuracy needed for clinical decision-making, especially in cases where subtle differences could impact treatment outcomes.
To address these challenges, the Index of Plaque Attenuation (IPA) emerged as a groundbreaking OCT-based technology. This innovative tool automatically assesses plaque stability after a single OCT pullback scan, requiring no additional consumables or procedural steps. It revolutionizes interventional cardiology by delivering a comprehensive and quantitative analysis of vulnerable plaques that allows for more precise treatment strategies, better risk assessment, and individualized management of patients with acute coronary syndrome.
IPA technology was unveiled at the 2024 iPCI conference in Rotterdam, the Netherlands. This prestigious event convened leading cardiovascular experts who explored the latest advancements in imaging and physiological technologies for cardiovascular intervention. Among the highlights was Professor Chenguang Li’s keynote on “Clinical Application of the Index of Plaque Attenuation (IPA) Based on OCT,” where he detailed the clinical implications of intravascular and molecular imaging in detecting vulnerable plaques and showcased the achievements of the IPA technology.

In his presentation, Professor Li emphasized that OCT remains the most advanced imaging tool available for intravascular imaging. He noted how IPA, a quantitative OCT-based tool, represents a significant leap forward in assessing plaque vulnerability. By providing accurate, objective data on plaque stability, IPA enables more effective stratification of patients, facilitating a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment that could greatly enhance patient outcomes.
In his presentation, Professor Li emphasized that OCT remains the most advanced imaging tool available for intravascular imaging. He noted how IPA, a quantitative OCT-based tool, represents a significant leap forward in assessing plaque vulnerability. By providing accurate, objective data on plaque stability, IPA enables more effective stratification of patients, facilitating a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment that could greatly enhance patient outcomes.

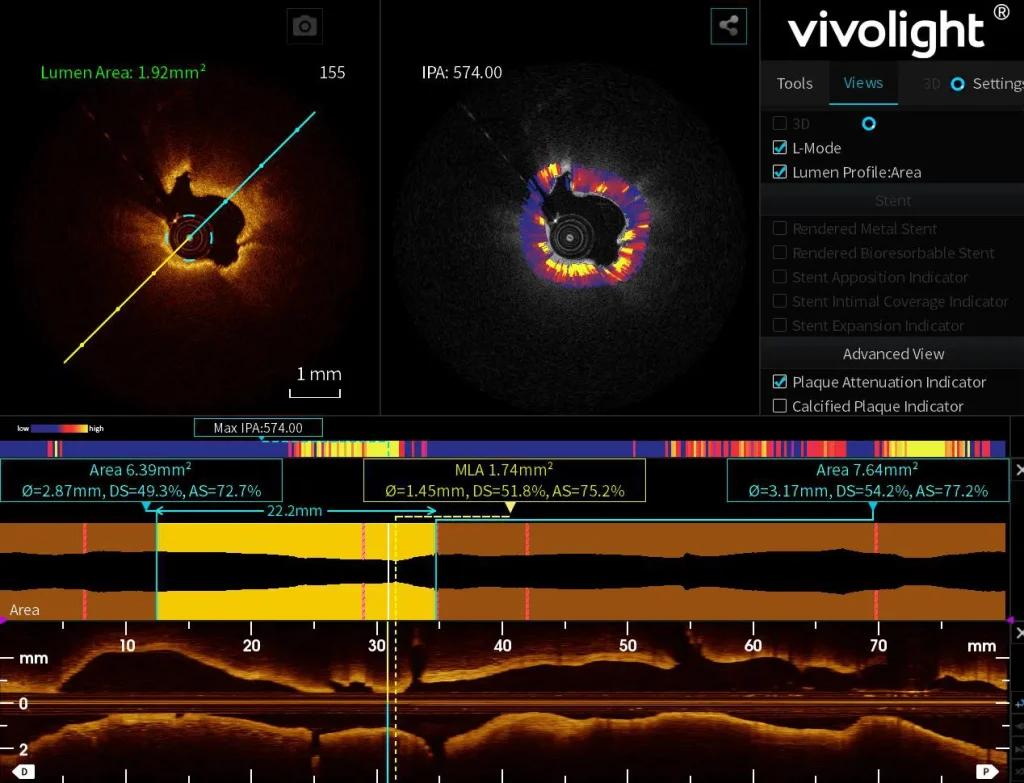
IPA uses unique light attenuation mapping to assess plaque vulnerability by analyzing how near-infrared light interacts with plaque components. Its color-coded results range from blue to red to yellow, visually indicating tissue optical characteristics. IPA highlights“positive”markers like thin-cap lipid plaques, macrophages, and cholesterol crystals while identifying“negative”markers such as more stable fibrous plaques by different colors. This color-coding helps clinicians better understand plaque composition and make informed, evidence-based decisions for interventions.
There is a growing interest among experts worldwide in this next-generation plaque stability assessment technology. The IPA’s integration into cardiovascular intervention could provide a more accurate, systematic approach to managing vulnerable plaques, potentially shifting the paradigm in cardiovascular medicine. Vivolight Medical has been proactive in further validating the IPA’s clinical impact through extensive randomized controlled trials (RCTs) across top-tier hospitals in China. These studies aim to solidify IPA’s clinical efficacy in predicting cardiovascular events, with the ultimate goal of establishing standardized thresholds for its use in regular practice.
Looking forward, Vivolight envisions a future where the IPA technology becomes a routine part of plaque assessment and management, driving advancements in precise medical strategy and patient-centered care. By bringing cutting-edge diagnostic capabilities to the forefront, Vivolight is positioning IPA as a crucial tool in reducing the incidence of cardiovascular events and enhancing the quality of life for patients globally. The dedication to continuous innovation and the relentless pursuit of excellence underscores Vivolight’s commitment to elevating cardiovascular health and reshaping the future of interventional cardiology.
Leave A Message
Scan to WhatsApp :
