
December 16, 2025 | Shaanxi, China — Tangdu Hospital, Air Force Medical University, in collaboration with Shenzhen Tsinghua University Research Institute, announced the clinical validation of CA-GPT, an AI decision-support system for optical coherence tomography (OCT)-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Results are reported in the preprint “COMPARE: Clinical Optimization with Modular Planning and Assessment via RAG-Enhanced AI-OCT: Superior Decision Support for Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Compared to ChatGPT-5 and Junior Operators.”

Optical coherence tomography (OCT) plays a central role in contemporary PCI planning and optimization, yet prior studies have shown only moderate inter-observer agreement for several critical OCT findings, even among experienced physicians (with reported correlation coefficients around 0.55–0.61). This variability can lead to inconsistent treatment strategies, particularly for complex coronary lesions.
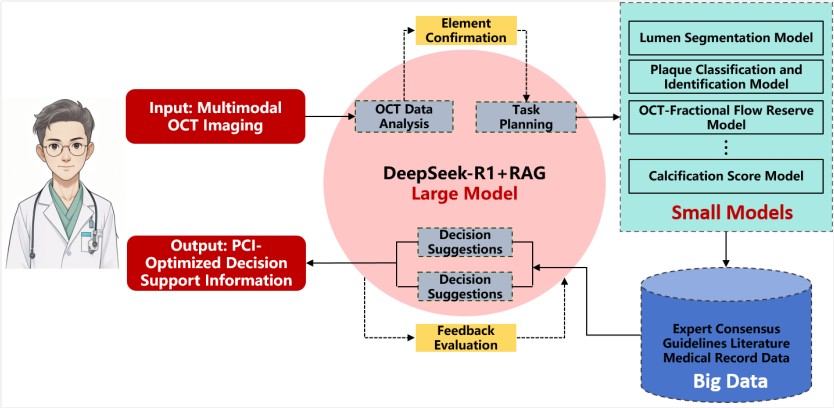
CA-GPT was developed to address this challenge by providing standardized, reproducible interpretation of OCT data and translating these findings into actionable clinical recommendations.
CA-GPT employs a two-layer architecture:
Imaging analysis layer: comprises 13 core analytical capabilities, all developed using deep-learning–based algorithms. Among them, six are independently developed, patented algorithms by the team, including:
● Automated vascular lumen segmentation and three-dimensional reconstruction
● Quantitative plaque tissue characterization, including fibrous, lipid-rich, and calcified plaques
● Automated identification of thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA)–type vulnerable plaques
● Stent apposition assessment
● Detection of stent edge dissection
● OCT-derived fractional flow reserve (OCT-FFR) computation, providing image-based coronary functional assessment
Retrieval-Augmented Reasoning Layer: Based on the open-source DeepSeek-R1 model and enhanced with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology, this layer enables the AI system to retrieve the most relevant guideline clauses and similar expert-labeled cases from a meticulously curated knowledge base. This comprehensive database includes international clinical guidelines, expert consensus statements, and over 100,000 expert-annotated PCI cases—ensuring the AI’s recommendations are not only traceable but also fully aligned with current clinical standards of care.
In a single-center analysis of consecutive OCT-guided PCI cases at Tangdu Hospital (June 2024–August 2025), 96 patients (160 lesions) were included. Clinical PCI strategygenerated by CA-GPT (raw OCT images as input) was compared with:
● a general-purpose LLM baseline (ChatGPT-5) prompted using manually extracted key parameters;
● four junior interventional cardiologists with 1–5 years of PCI experience.
All outputs were benchmarked against the actual procedure record performed by a senior operator (>10 years’ experience; ≥200 PCI cases/year). Ten prespecified criteria were assessed—five for pre-PCI planning and five for post-PCI evaluation—scored by agreement (0–5 per phase).
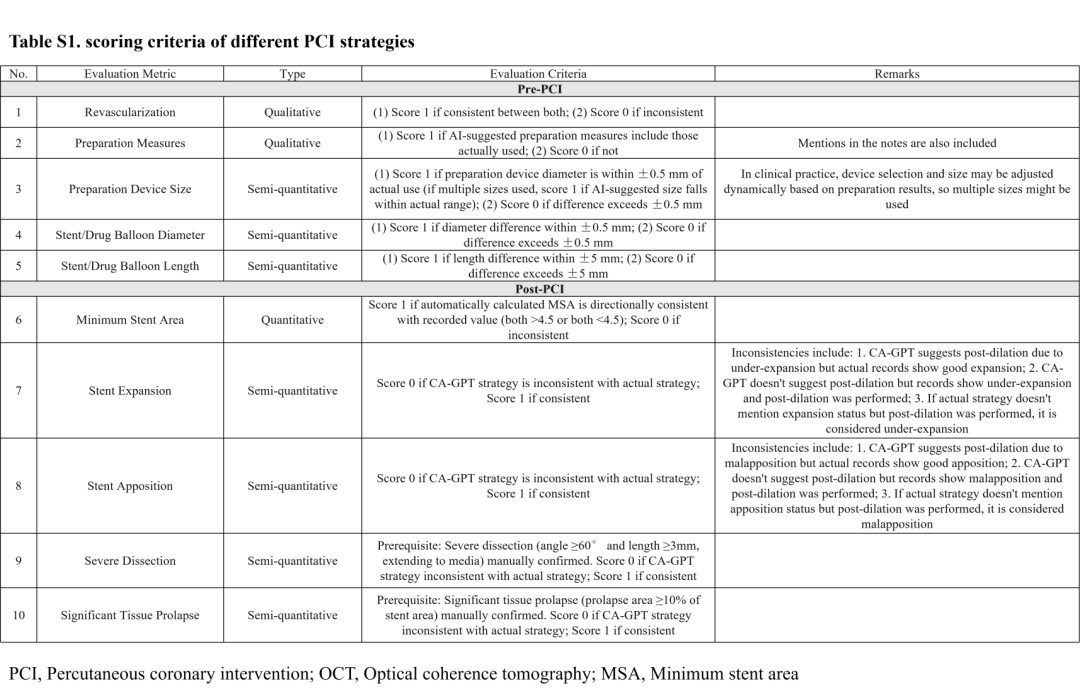
Key results:
● Pre-PCI planning: During pre-procedural planning, CA-GPT achieved a median agreement score of 5 (out of 5), significantly outperforming ChatGPT-5 (median score: 3) and junior physicians (median score: 4).
Performance across key decision points was as follows:
● Stent diameter selection (tolerance ±0.5 mm): CA-GPT achieved an accuracy of 90.3%, exceeding that of junior physicians (72.2%) and ChatGPT-5 (63.9%).
● Stent length selection (tolerance ±5 mm): CA-GPT achieved an accuracy of 80.6%, significantly higher than that of junior physicians (52.8%).
● Pre-dilation device selection: CA-GPT achieved an accuracy of 73.6%, representing a substantial improvement over ChatGPT-5 (37.5%).
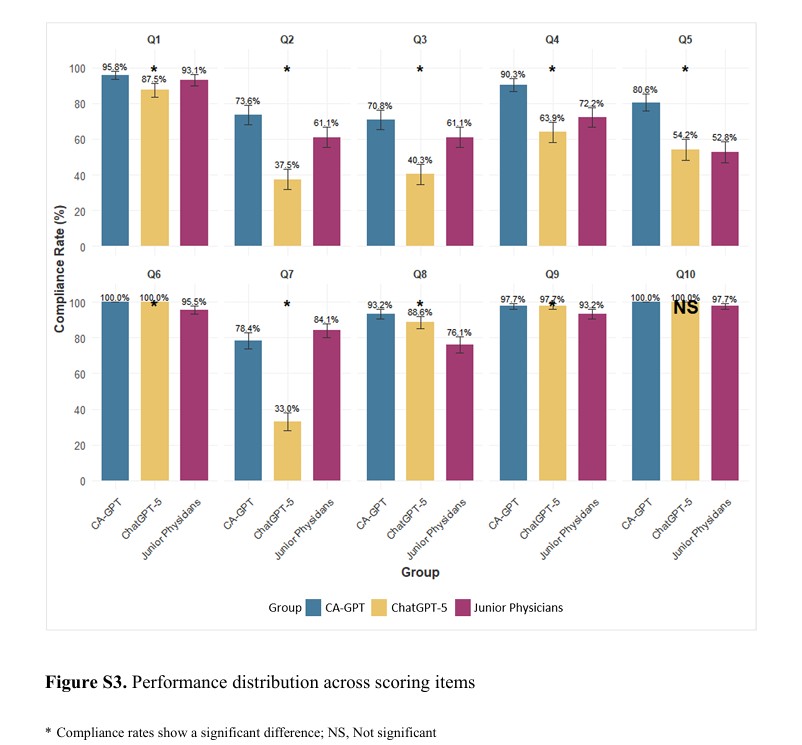
● Post-PCI evaluation: CA-GPT maintained a median score of 5/5 and achieved 93.2% accuracy in stent apposition assessment, compared with 76.1% for junior physicians, demonstrating higher precision and consistency.
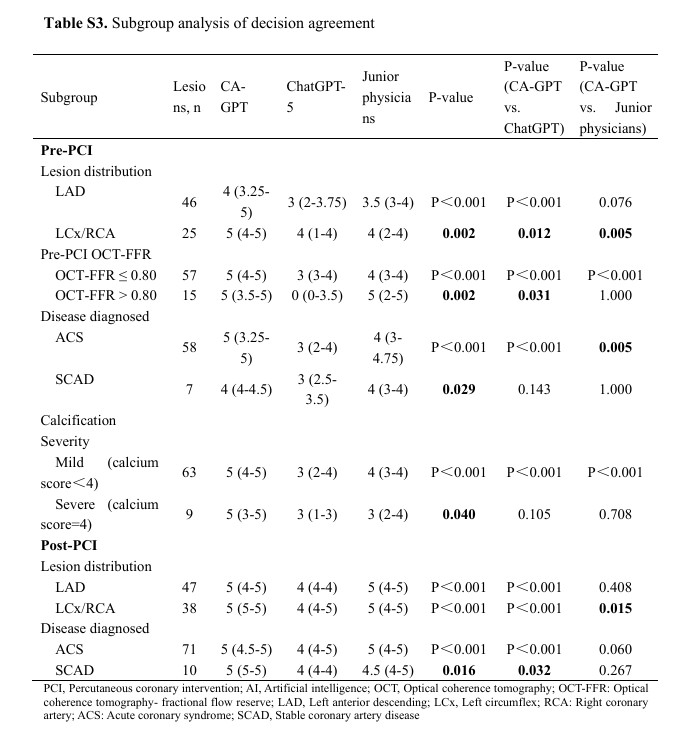
● Robustness in complex scenarios: Subgroup analyses indicated CA-GPT’s advantage was most pronounced in more challenging settings, including ischemia-significant lesions (OCT-FFR ≤0.80) and ACS cases.
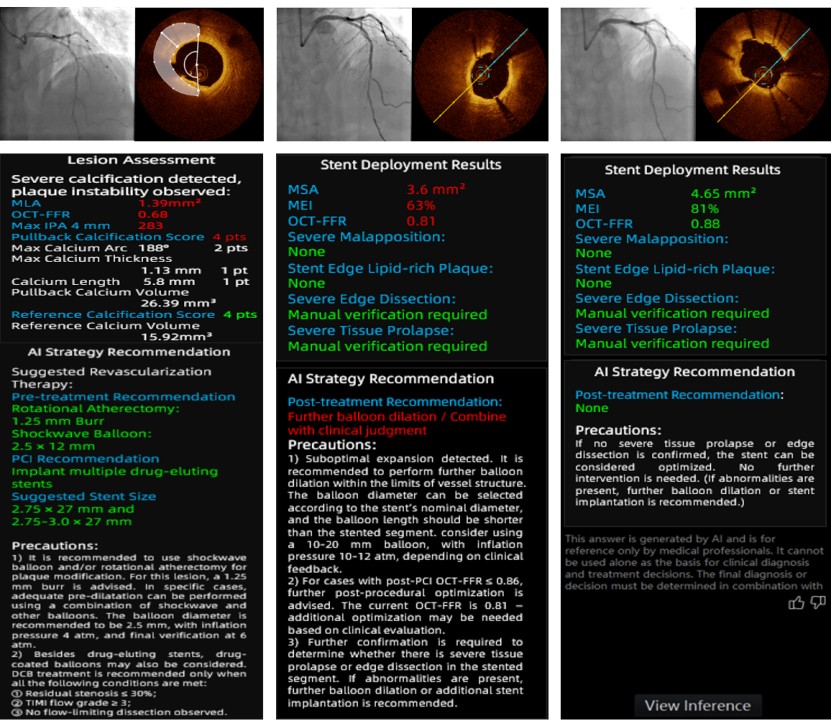
Unlike generic LLMs, CA-GPT grounds its reasoning in validated imaging features and authoritative clinical evidence. The retrieval-augmented approach enables traceable decision paths, reduces the risk of unsupported or non-evidence-based recommendations, and ensures alignment with current standards of care.
The observed performance gap highlights a fundamental limitation of general-purpose LLMs in interventional cardiology: without structured imaging intelligence and domain-specific retrieval, linguistic fluency alone is insufficient for high-stakes procedural decision-making.
To the team’s knowledge, CA-GPT represents one of the first clinically validated systems to integrate OCT-specific artificial intelligence with retrieval-augmented language modeling for comprehensive PCI decision support.
By improving consistency in OCT interpretation and narrowing the expertise gap between junior and senior physicians, CA-GPT has the potential to enhance procedural quality and patient safety in interventional cardiology. The researchers emphasize that CA-GPT is intended as a decision-support tool, augmenting—not replacing—clinical judgment.
Leave A Message
Scan to WhatsApp :
